TLMモデルからSystemCモデルへの7つの課題
Merry Christmas!!!
SystemCでは幅広い範囲の抽象度で記述することができます。
それではそれぞれのモデルを再度は以下のような感じになります。
モデリング例
- Cycleモデル
#include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> using namespace std; #include <systemc.h> SC_MODULE( hoge ) { sc_in <bool > clk; sc_in <bool > xrst; sc_in <bool > ce; sc_in <bool > we; sc_in <sc_uint<10> > address; sc_in <sc_uint<32> > wdata; sc_out <sc_uint<32> > rdata; vector<unsigned int> mem; unsigned int mem_size; void process(); void write(unsigned int, unsigned int); unsigned int read(unsigned int); SC_CTOR( hoge ) : clk("clk"), xrst("xrst"), ce("ce"), we("we") , address("address"), wdata("wdata"), rdata("rdata") { SC_THREAD(process); sensitive << clk.pos(); async_reset_signal_is(xrst, false); // Size Of Memory 32bit x 256word mem_size = 0x100; mem.resize(mem_size); for(unsigned int i=0; i<mem_size; i++){ mem[i] = 0; } } }; inline void hoge::process(){ rdata.write(0); wait(); while (true) { if ((ce.read() == 1)) { unsigned int _adrs = address.read() >> 2; if (we.read() == 1) { unsigned int _data = wdata.read(); write(_adrs, _data); } else { rdata = read(_adrs); } } else { wait(); } } } inline void hoge::write(unsigned int _adrs, unsigned int _data){ mem[_adrs] = _data; wait(); } inline unsigned int hoge::read(unsigned int _adrs){ wait(); wait(); return mem[_adrs]; }
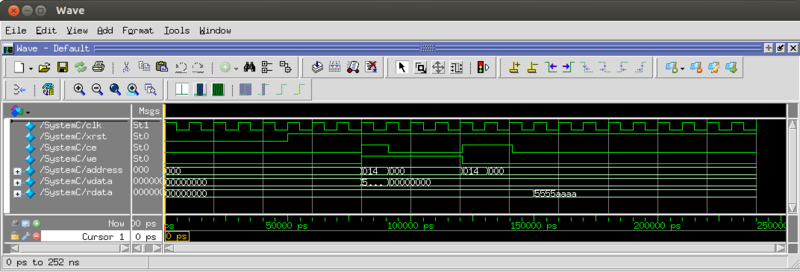
- 実行波形
- TLMモデル
#include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> using namespace std; #include <systemc.h> #include <tlm.h> #include "tlm_utils/simple_target_socket.h" using namespace tlm; SC_MODULE( hoge ) { tlm_utils::simple_target_socket<hoge, 32> target_socket; vector<unsigned int> mem; unsigned int mem_size; void my_b_transport(tlm_generic_payload&, sc_time&); void write(unsigned int, unsigned int); unsigned int read(unsigned int); SC_CTOR( hoge ) : target_socket("target_socket") { target_socket.register_b_transport(this, &hoge::my_b_transport); // Size Of Memory 32bit x 256word mem_size = 0x100; mem.resize(mem_size); for(unsigned int i=0; i<mem_size; i++){ mem[i] = 0; } } }; inline void hoge::my_b_transport(tlm_generic_payload& trans, sc_time& delay){ sc_dt::uint64 adr = trans.get_address() >> 2; unsigned char* ptr = trans.get_data_ptr(); unsigned int len = trans.get_data_length(); unsigned int _tmp; if (trans.is_read()) { delay += sc_time(30, SC_NS); _tmp = read(adr); memcpy(ptr, &_tmp, len); } else if (trans.is_write()) { delay += sc_time(10, SC_NS); memcpy( &_tmp, ptr, len); write(adr, _tmp); } else { delay += SC_ZERO_TIME; } trans.set_dmi_allowed(false); trans.set_response_status( tlm::TLM_OK_RESPONSE ); } inline void hoge::write(unsigned int _adrs, unsigned int _data){ mem[_adrs] = _data; } inline unsigned int hoge::read(unsigned int _adrs){ return mem[_adrs]; }
差分はなにか?
例えば、 #define で記述するような場合はこんな感じです。
#include <stdlib.h> #include <vector> using namespace std; #include <systemc.h> //###################################################################// //# 1.Include //###################################################################// #ifdef TLM #include "tlm_utils/simple_target_socket.h" using namespace tlm; #endif //###################################################################// SC_MODULE( hoge ) { //###################################################################// //# 2.Interface //###################################################################// #ifdef TLM tlm_utils::simple_target_socket<hoge, 32> target_socket; #else sc_in <bool > clk; sc_in <bool > xrst; sc_in <bool > ce; sc_in <bool > we; sc_in <sc_uint<10> > address; sc_in <sc_uint<32> > wdata; sc_out <sc_uint<32> > rdata; #endif //###################################################################// vector<unsigned int> mem; unsigned int mem_size; //###################################################################// //# 3.process関数 //###################################################################// #ifdef TLM void my_b_transport(tlm_generic_payload&, sc_time&); #else void process(); #endif void write(unsigned int, unsigned int); unsigned int read(unsigned int); //###################################################################// SC_CTOR( hoge ) //###################################################################// //# 4.初期化リスト //###################################################################// #ifdef TLM : target_socket("target_socket") #else : clk("clk"), xrst("xrst"), ce("ce"), we("we") , address("address"), wdata("wdata"), rdata("rdata") #endif //###################################################################// { //###################################################################// //# 5.process起動条件 //###################################################################// #ifdef TLM target_socket.register_b_transport(this, &hoge::my_b_transport); #else SC_THREAD(process); sensitive << clk.pos(); async_reset_signal_is(xrst, false); #endif //###################################################################// // Size Of Memory 32bit x 256word mem_size = 0x100; mem.resize(mem_size); for(unsigned int i=0; i<mem_size; i++){ mem[i] = 0; } } }; //###################################################################// //# 6.process(処理) //###################################################################// #ifdef TLM inline void hoge::my_b_transport(tlm_generic_payload& trans, sc_time& delay){ sc_dt::uint64 adr = trans.get_address() >> 2; unsigned char* ptr = trans.get_data_ptr(); unsigned int len = trans.get_data_length(); unsigned int _tmp; if (trans.is_read()) { delay += sc_time(30, SC_NS); _tmp = read(adr); memcpy(ptr, &_tmp, len); } else if (trans.is_write()) { delay += sc_time(10, SC_NS); memcpy( &_tmp, ptr, len); write(adr, _tmp); } else { delay += SC_ZERO_TIME; } trans.set_dmi_allowed(false); trans.set_response_status( tlm::TLM_OK_RESPONSE ); } #else inline void hoge::process(){ rdata.write(0); wait(); while (true) { if ((ce.read() == 1)) { unsigned int _adrs = address.read() >> 2; if (we.read() == 1) { unsigned int _data = wdata.read(); write(_adrs, _data); } else { rdata = read(_adrs); } } else { wait(); } } } #endif //###################################################################// inline void hoge::write(unsigned int _adrs, unsigned int _data){ mem[_adrs] = _data; //###################################################################// //# 7.Timing //###################################################################// #ifndef TLM wait(); #endif //###################################################################// } inline unsigned int hoge::read(unsigned int _adrs){ //###################################################################// //# 7.Timing //###################################################################// #ifndef TLM wait(); wait(); #endif //###################################################################// return mem[_adrs]; }
まとめ
理想的な設計フローとして、TLMモデルから SystemCモデルにする場合に課題点についてでした。 ただ、これらの課題は簡単に解決するものもあるし、更に追求していくともっと壁があると思います(笑)
- 課題点
1. Include
2. Interface
3. process関数
4. 初期化リスト
5. process起動条件
6. process(処理)
7. Timing